Urgent patient transport.
Data
44 ambulances, Girona region.
Method
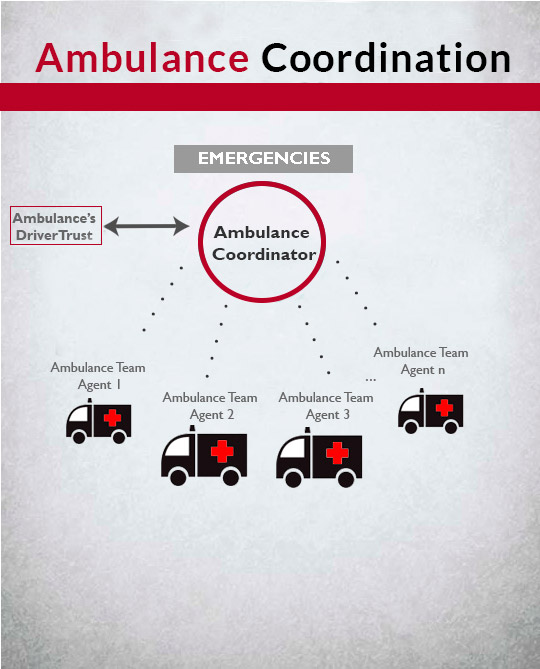
Agent-based system, Fuzzy filtering regarding ambulance trust; Region coverage.
Results
99,5 % arrivals within 15’.
Emergency transportation on specialized vehicles is needed when a person’s health is in risk of irreparable damage. In rural regions, studies have shown that ambulance teams have different response times, mainly because of the drivers’ expertise. The challenge for the regional authorities is to appropriately coordinate their resources to continuously improve response time, taking into account the resources needed and driver expertise. In response, we developed a multi-agent system that maintain the real distributed organization of resources. To solve the assignment problem (which ambulance agent attends a patient request), we use an auction mechanism and a region coverage algorithm. Driver skills are represented by trust, and ambulance response times are modulated by them.
Programmed patient transport.
Data
700 daily routes, 80 ambulances.
Method
Metaheuristic method.
Results
Product on exploitation (IrisAmb by Lafcarr); Spin-off(Newronia)
The daily programming of patient transport to hospitals and healthcare places due to specific treatments has been carried out for a long time manually, and based on human experts. To automate the system, we develop an optimization engine based on metaheuristics. The systems allows the automatic scheduling of medical transportation services considering a set of constraints as the needs of the user (stretcher or sitting service, individual or collective, equipment, etc.), compliance with current legislation, waiting time and length of service bounded, and the limited availability of resources (ambulance drivers). The system proposes the sequences of services to be done and which ambulance should be carried them out, according to different optimization criteria: kilometres, waiting time of patients, ambulances used.